Table of Contents
This journey ventures into the possibilities and prospects of Artificial Intelligence (AI), which is changing the game in industries such as healthcare and entertainment.
• The Origins and Evolution of AI
AI, named by Alan Turing and John McCarthy in 1956, began in the middle of the 20th century with the Turing Test. Problem-solving and logical reasoning were the emphasis of early AI. Despite some years of stagnation, computing technologies’ growth and data explosion in the 2000s revived interest, driving AI into its contemporary boom, which cross-links with machine learning, neural networks, and data analytics.
• AI in Everyday Life
AI is transforming our daily lives, enhancing tasks, managing online shopping, entertainment, healthcare, and education. Personal assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant manage tasks, while online shopping and social media platforms customize feeds. AI also aids in healthcare diagnosis, trend prediction, and personalized treatment plans. In education, adaptive learning platforms cater to individual learning styles, and chatbots provide 24/7 assistance.
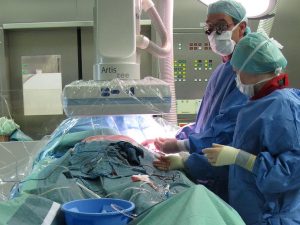
• The Role of AI in Healthcare
The role of AI in medicine is nothing less than revolutionary. It helps to diagnose illnesses with unprecedented precision, even surpassing that of doctors. Machine learning algorithms process medical images, including X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, to detect abnormalities such as tumors and breaks. They are particularly useful in areas such as radiology and pathology where early diagnosis is important.
AI-driven predictive analytics predicts health outcomes and aids early intervention in diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and mental illness. AI facilitates personalized medicine based on a person’s genetic profile by processing and interpreting large sets of genetic data, resulting in more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
AI-controlled robotic surgeries improve accuracy and minimize human error, leading to improved patient outcomes and quicker recovery times. Virtual health assistants and chatbots answer patients’ real-time questions, schedule appointments, and alert patients to their medication. This eases the burden on healthcare systems and enables more tailored patient care.
AI is also vital to drug development and discovery. By modeling molecular structures and biological processes, AI can forecast how new drugs will act in the body, vastly accelerating the research stage and lowering costs. The future of healthcare is immense with the role of AI, promising a day when medical care is more predictive, personal, and preventive.
• Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Even with the unparalleled potential of AI, it also presents various challenges and ethical issues that need to be addressed. One of the more important concerns is the question of bias and fairness. Many AI algorithms are trained on past data that contains biases and, hence, replicate discriminatory practices in hiring, lending, and policing. Unbiased and fair AI systems need diverse and representative datasets and ongoing checks.
Privacy is also a serious concern. With AI systems handling large volumes of personal data, the potential for data breaches and misuse of information is great. Protecting privacy entails strong data protection legislation, secure encryption practices, and open data usage policies.
The threat of job loss is common, given that AI systems and automation can execute tasks previously reserved for humans. Although AI can generate new forms of jobs, there should be emphasis on reskilling and upskilling the workforce in order to fit new job profiles.
Ethical issues also apply to AI decision-making. Self-driving vehicles, for instance, present ethical challenges where moral judgment is needed. Having guidelines and standards for ethical AI usage becomes important to help them navigate the intricacies.
Last but not least is the issue of transparency and accountability. The more complex AI systems get, the harder it is to understand their decision-making processes. Having transparency in AI algorithms and making developers and users accountable for what they do will promote building trust and reliability in AI technologies
• The Future of AI: What’s Next?
The future of AI promises unimaginable changes. Perhaps most eagerly awaited is the creation of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), designed to display human-like intelligence on a wide variety of tasks. AGI has the potential to change many industries by enabling the automation of complicated problem-solving and decision-making.
AI also stands to evolve in fields such as natural language processing (NLP) and emotional intelligence. Future AI will be able to comprehend and address human emotions, making interactions more intuitive and empathetic. In the healthcare industry, AI stands to revolutionize personalized medicine, predictive care, and possibly even the curing of diseases that are currently untreatable.
Quantum computing is another horizon for AI, providing exponentially more powerful computation to address intricate problems that are not solvable by today’s computers. This may hasten AI technology and applications in cryptography, materials science, and pharmaceuticals.
Collaboration among AI and other cutting-edge technologies, including the Internet of Things (IoT) and blockchain, will yield new solutions for smart cities, supply chains, and more. AI-driven drones and robots will be used in disaster relief, agriculture, logistics, and others.
But to make these future developments possible will involve sustained research, ethical examination, and interdisciplinary collaborations. The future of AI is exciting as well as challenging, one that will transform our world in ways we are only just starting to conceive.
